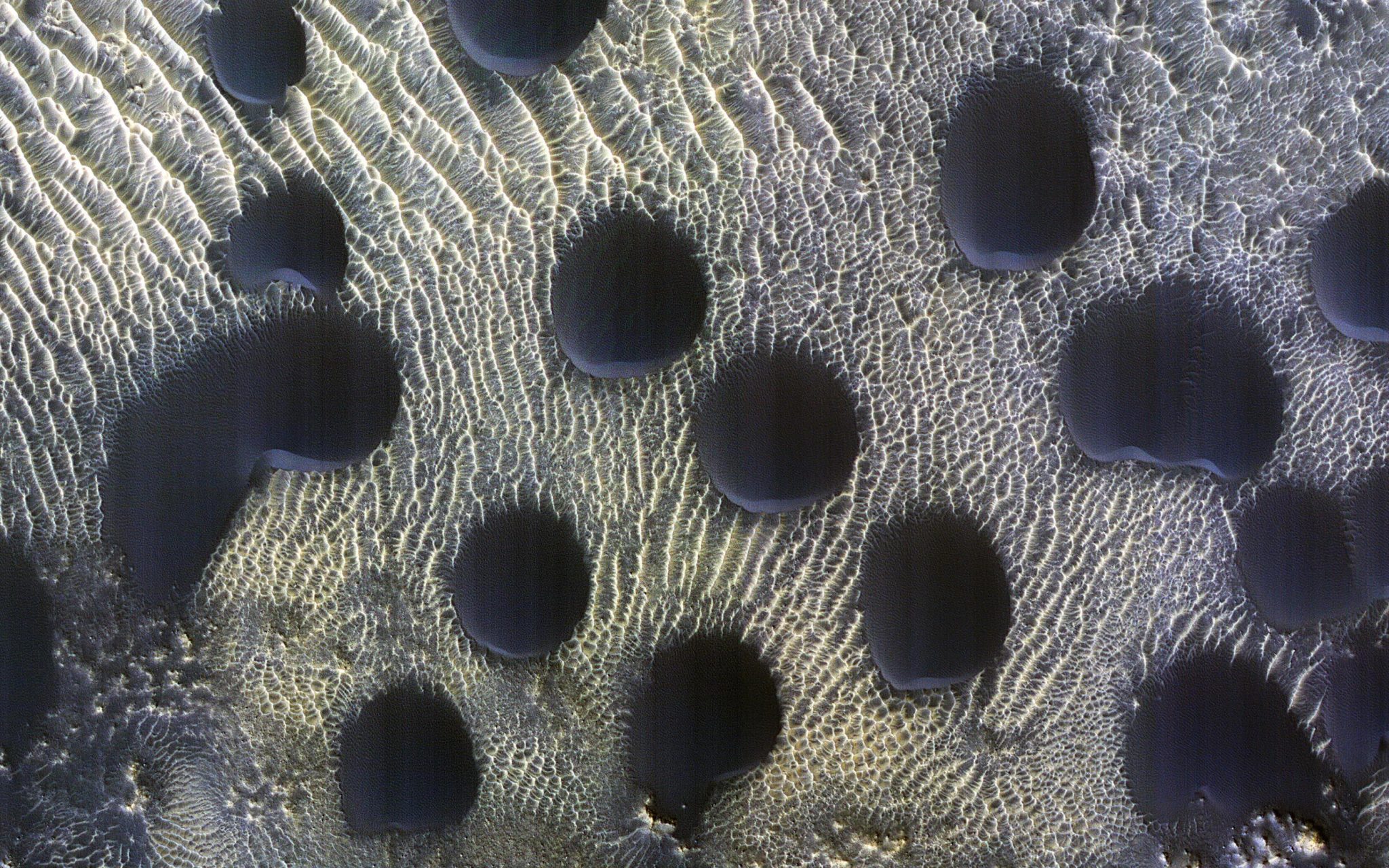
Las dunas de arena de muchas formas y tamaños son comunes en Marte. En este ejemplo, las dunas son casi perfectamente circulares, lo cual es inusual. Crédito: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Universidad de Arizona
Las dunas de arena de muchas formas y tamaños son comunes en[{» attribute=»»>Mars. In this example, the dunes are almost perfectly circular, which is unusual.
They are still slightly asymmetrical, with steep slip faces on the south ends. This indicates that sand generally moves to the south, but the winds may be variable.

Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona
This is part of a series of images (see above) to monitor how frost disappears in the late winter; this observation appears to be free of frost. A previous image (below) shows when the surface was covered by frost.

Circular sand dunes on Mars captured by the Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona
The map is projected here at a scale of 25 centimeters (9.8 inches) per pixel. (The original image scale is 30.3 centimeters [11.9 inches] por píxel [with 1 x 1 binning]; objetos alrededor de 91 centímetros [35.8 inches] se resuelven.) El norte está arriba.

El mapa se proyecta aquí a una escala de 25 centímetros (9,8 pulgadas) por píxel. (La escala de la imagen original es de 30,3 centímetros [11.9 inches] por píxel [with 1 x 1 binning]; objetos alrededor de 91 centímetros [35.8 inches] se resuelven.) El norte está arriba. Crédito: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Universidad de Arizona
HiRISE significa Experimento científico de imágenes de alta resolución. Este es un sistema de cámara a bordo del Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, que es una nave espacial que orbita Marte. HiRISE es la cámara más grande y poderosa jamás enviada a otro planeta, y está diseñada para capturar imágenes increíblemente detalladas de la superficie marciana. Su alta resolución permite a los científicos estudiar la geología, la mineralogía y la topografía del planeta con mucho más detalle que nunca.

Concepto artístico de Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Crédito: JPL/NASA
El Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) es una nave espacial lanzada por[{» attribute=»»>NASA in 2005 to study Mars. The main goal of the MRO mission is to understand the geology, climate, and search for signs of water and potentially habitable environments on Mars. The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments, including the HiRISE camera, as well as radar, spectrometers, and other sensors. The MRO orbits Mars in a highly elliptical polar orbit, which allows it to image the planet’s surface and atmosphere, study its geology and mineralogy, and search for signs of water and other resources. The mission has been ongoing since its launch and has made numerous discoveries and advancements in our understanding of Mars.
The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
También te puede interesar
-
Llame a fotógrafos y astrónomos de Wicklow para obtener fotografías extraordinarias
-
Cómo el pensamiento visuoespacial mejora la comprensión de la química | Noticias
-
La cápsula Starliner da un gran paso hacia el primer vuelo tripulado
-
Los satélites Tiandu de China realizan experimentos de transmisión y enrutamiento Tierra-Luna_China.org.cn
-
Esta semana en astronomía con Dave Eicher